开源软件名称(OpenSource Name): json4s/json4s开源软件地址(OpenSource Url): https://github.com/json4s/json4s开源编程语言(OpenSource Language):
Scala
96.2%
开源软件介绍(OpenSource Introduction):
At this moment there are at least 6 json libraries for scala, not counting the java json libraries.
All these libraries have a very similar AST. This project aims to provide a single AST to be used by other scala
json libraries.
At this moment the approach taken to working with the AST has been taken from lift-json and the native package
is in fact lift-json but outside of the lift project.
This project also attempts to set lift-json free from the release schedule imposed by the lift framework.
The Lift framework carries many dependencies and as such it's typically a blocker for many other scala projects when
a new version of scala is released.
So the native package in this library is in fact verbatim lift-json in a different package name; this means that
your import statements will change if you use this library.
import org .json4s ._
import org .json4s .native .JsonMethods ._ After that everything works exactly the same as it would with lift-json
In addition to the native parser there is also an implementation that uses jackson for parsing to the AST.
The jackson module includes most of the jackson-module-scala functionality and the ability to use it with the
lift-json AST.
To use jackson instead of the native parser:
import org .json4s ._
import org .json4s .jackson .JsonMethods ._ Be aware that the default behavior of the jackson integration is to close the stream when it's done.
If you want to change that:
import com .fasterxml .jackson .databind .SerializationFeature
org.json4s.jackson.JsonMethods .mapper.configure(SerializationFeature .CLOSE_CLOSEABLE , false )Parsing and formatting utilities for JSON.
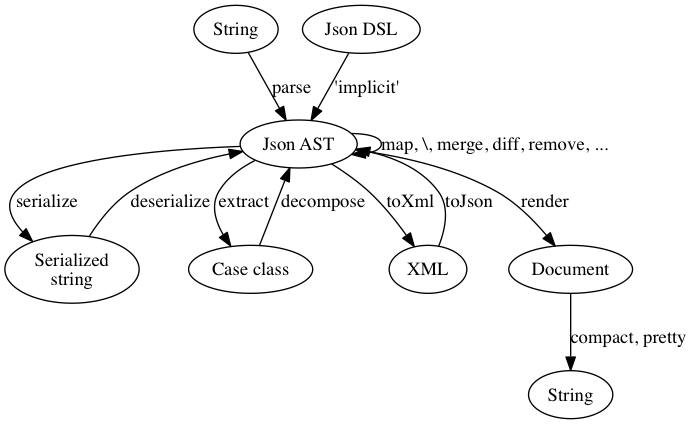
A central concept in lift-json library is Json AST which models the structure of
a JSON document as a syntax tree.
sealed abstract class JValue
case object JNothing extends JValue // 'zero' for JValuecase object JNull extends JValue
case class JString (s : String ) extends JValue
case class JDouble (num : Double ) extends JValue
case class JDecimal (num : BigDecimal ) extends JValue
case class JInt (num : BigInt ) extends JValue
case class JLong (num : Long ) extends JValue
case class JBool (value : Boolean ) extends JValue
case class JObject (obj : List [JField ]) extends JValue
case class JArray (arr : List [JValue ]) extends JValue
type JField = (String , JValue )All features are implemented in terms of the above AST. Functions are used to transform
the AST itself, or to transform the AST between different formats. Common transformations
are summarized in a following picture.
Summary of the features:
Fast JSON parser
LINQ-style queries
Case classes can be used to extract values from parsed JSON
Diff & merge
DSL to produce valid JSON
XPath-like expressions and HOFs to manipulate JSON
Pretty and compact printing
XML conversions
Serialization
Low-level pull parser API
You can add the json4s as a dependency in following ways. Note, replace {latestVersion} with correct Json4s version.
You can find available versions here:
https://search.maven.org/search?q=org.json4s
For the native support add the following dependency to your project description:
val json4sNative = " org.json4s" %% " json4s-native" % " {latestVersion}" For the Jackson support add the following dependency to your project description:
val json4sJackson = " org.json4s" %% " json4s-jackson" % " {latestVersion}" For the native support add the following dependency to your pom:
<dependency >
<groupId >org.json4s</groupId >
<artifactId >json4s-native_${scala.version}</artifactId >
<version >{latestVersion}</version >
</dependency > For the jackson support add the following dependency to your pom:
<dependency >
<groupId >org.json4s</groupId >
<artifactId >json4s-jackson_${scala.version}</artifactId >
<version >{latestVersion}</version >
</dependency > Extras
Support for Enum, Joda-Time, Java 8 Date & Time...
Applicative style parsing with Scalaz
Any valid json can be parsed into internal AST format.
For native support:
scala> import org .json4s ._
scala> import org .json4s .native .JsonMethods ._
scala> parse(""" { "numbers" : [1, 2, 3, 4] } """ : org.json4s.JValue =
JObject (List ((numbers,JArray (List (JInt (1 ), JInt (2 ), JInt (3 ), JInt (4 ))))))
scala> parse(""" {"name":"Toy","price":35.35}""" = true )
res1: org.json4s.JValue =
JObject (List ((name,JString (Toy )), (price,JDecimal (35.35 )))) For jackson support:
scala> import org .json4s ._
scala> import org .json4s .jackson .JsonMethods ._
scala> parse(""" { "numbers" : [1, 2, 3, 4] } """ : org.json4s.JValue =
JObject (List ((numbers,JArray (List (JInt (1 ), JInt (2 ), JInt (3 ), JInt (4 ))))))
scala> parse(""" {"name":"Toy","price":35.35}""" = true )
res1: org.json4s.JValue =
JObject (List ((name,JString (Toy )), (price,JDecimal (35.35 )))) You can generate json in 2 modes: either in DoubleMode or in BigDecimalMode; the former will map all decimal values
into JDoubles, and the latter into JDecimals.
For the double mode dsl use:
import org .json4s .JsonDSL ._
// orimport org .json4s .JsonDSL .WithDouble ._ For the big decimal mode dsl use:
import org .json4s .JsonDSL .WithBigDecimal ._
Primitive types map to JSON primitives.
Any seq produces JSON array.
scala> val json = List (1 , 2 , 3 )
scala> compact(render(json))
res0: String = [1 ,2 ,3 ]
Tuple2[String, A] produces field.
scala> val json = (" name" - > " joe" > compact(render(json))
res1: String = {" name" : " joe"
~ operator produces object by combining fields.
scala> val json = (" name" - > " joe" ~ (" age" - > 35 )
scala> compact(render(json))
res2: String = {" name" : " joe" " age" : 35 }
~~ operator works the same as ~ and is useful in situations where ~ is shadowed, eg. when using Spray or akka-http.
scala> val json = (" name" - > " joe" ~~ (" age" - > 35 )
scala> compact(render(json))
res2: String = {" name" : " joe" " age" : 35 }
Any value can be optional. The field and value are completely removed when it doesn't have a value.
scala> val json = (" name" - > " joe" ~ (" age" - > Some (35 ))
scala> compact(render(json))
res3: String = {" name" : " joe" " age" : 35 }
scala> val json = (" name" - > " joe" ~ (" age" - > (None : Option [Int ]))
scala> compact(render(json))
res4: String = {" name" : " joe" To extend the dsl with your own classes you must have an implicit conversion in scope of signature:
type DslConversion = T => JValue import org .json4s ._
import org .json4s .JsonDSL ._
import org .json4s .jackson .JsonMethods ._
case class Winner (id : Long , numbers : List [Int ])
case class Lotto (id : Long , winningNumbers : List [Int ], winners : List [Winner ], drawDate : Option [java.util.Date ])
object JsonExample {
val winners = List (Winner (23 , List (2 , 45 , 34 , 23 , 3 , 5 )), Winner (54 , List (52 , 3 , 12 , 11 , 18 , 22 )))
val lotto = Lotto (5 , List (2 , 45 , 34 , 23 , 7 , 5 , 3 ), winners, None )
val json =
(" lotto" - >
(" lotto-id" - > lotto.id) ~
(" winning-numbers" - > lotto.winningNumbers) ~
(" draw-date" - > lotto.drawDate.map(_.toString)) ~
(" winners" - >
lotto.winners.map { w =>
((" winner-id" - > w.id) ~
(" numbers" - > w.numbers))}))
def main (args : Array [String ]): Unit = {
println(compact(render(json)))
}
}scala> JsonExample .main(Array .empty[String ])
{" lotto" : {" lotto-id" : 5 ," winning-numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,7 ,5 ,3 ]," winners" :
[{" winner-id" : 23 ," numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,3 ,5 ]},{" winner-id" : 54 ," numbers" : [52 ,3 ,12 ,11 ,18 ,22 ]}]}} The above example produces the following pretty-printed JSON. Notice that draw-date field is not rendered since its value is None:
scala> pretty(render(JsonExample .json))
{
" lotto" : {
" lotto-id" : 5 ,
" winning-numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,7 ,5 ,3 ],
" winners" : [{
" winner-id" : 23 ,
" numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,3 ,5 ]
},{
" winner-id" : 54 ,
" numbers" : [52 ,3 ,12 ,11 ,18 ,22 ]
}]
}
} Two JSONs can be merged and diffed with each other.
Please see more examples in MergeExamples.scala and DiffExamples.scala .
scala> import org .json4s ._
scala> import org .json4s .jackson .JsonMethods ._
scala> val lotto1 = parse(""" { "lotto":{
"lotto-id":5,
"winning-numbers":[2,45,34,23,7,5,3],
"winners":[{
"winner-id":23,
"numbers":[2,45,34,23,3,5]
}]
}
}""" )
scala> val lotto2 = parse(""" { "lotto":{
"winners":[{
"winner-id":54,
"numbers":[52,3,12,11,18,22]
}]
}
}""" )
scala> val mergedLotto = lotto1 merge lotto2
scala> pretty(render(mergedLotto))
res0: String =
{
" lotto" : {
" lotto-id" : 5 ,
" winning-numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,7 ,5 ,3 ],
" winners" : [{
" winner-id" : 23 ,
" numbers" : [2 ,45 ,34 ,23 ,3 ,5 ]
},{
" winner-id" : 54 ,
" numbers" : [52 ,3 ,12 ,11 ,18 ,22 ]
}]
}
}
scala> val Diff (changed, added, deleted) = mergedLotto diff lotto1
changed: org.json4s.JValue = JNothing
added: org.json4s.JValue = JNothing
deleted: org.json4s.JValue = JObject (List ((lotto,JObject (List (JField (winners,
JArray (List (JObject (List ((winner- id,JInt (54 )), (numbers,JArray (
List (JInt (52 ), JInt (3 ), JInt (12 ), JInt (11 ), JInt (18 ), JInt (22 )))))))))))))) JSON values can be extracted using for-comprehensions.
Please see more examples in JsonQueryExamples.scala .
scala> import org .json4s ._
scala> import org .json4s .native .JsonMethods ._
scala> val json = parse(""" { "name": "joe",
"children": [
{
"name": "Mary",
"age": 5
},
{
"name": "Mazy",
"age": 3
}
]
}
""" )
scala> for {
JObject (child) < - json
JField (" age" JInt (age)) < - child
} yield age
res0: List [BigInt ] = List (5 , 3 )
scala> for {
JObject (child) < - json
JField (" name" JString (name)) < - child
JField (" age" JInt (age)) < - child
if age > 4
} yield (name, age)
res1: List [(String , BigInt )] = List ((Mary ,5 )) The json AST can be queried using XPath-like functions. The following REPL session shows the usage of
'\', '\\', 'find', 'filter', 'transform', 'remove' and 'values' functions.
The example json is:
{
"person" : {
"name" : "Joe" ,
"age" : 35 ,
"spouse" : {
"person" : {
"name" : "Marilyn" ,
"age" : 33
}
}
}
} Translated to DSL syntax:
scala> import org .json4s ._
scala> import org .json4s .native .JsonMethods ._ or
scala> import org .json4s .jackson .JsonMethods ._
scala> import org .json4s .JsonDSL ._
scala> val json : JObject =
(" person" - >
(" name" - > " Joe" ~
(" age" - > 35 ) ~
(" spouse" - >
(" person" - >
(" name"
六六分期app的软件客服如何联系?不知道吗?加qq群【895510560】即可!标题:六六分期
阅读:19606| 2023-10-27
今天小编告诉大家如何处理win10系统火狐flash插件总是崩溃的问题,可能很多用户都不知
阅读:10097| 2022-11-06
今天小编告诉大家如何对win10系统删除桌面回收站图标进行设置,可能很多用户都不知道
阅读:8400| 2022-11-06
今天小编告诉大家如何对win10系统电脑设置节能降温的设置方法,想必大家都遇到过需要
阅读:8756| 2022-11-06
我们在使用xp系统的过程中,经常需要对xp系统无线网络安装向导设置进行设置,可能很多
阅读:8708| 2022-11-06
今天小编告诉大家如何处理win7系统玩cf老是与主机连接不稳定的问题,可能很多用户都不
阅读:9754| 2022-11-06
电脑对日常生活的重要性小编就不多说了,可是一旦碰到win7系统设置cf烟雾头的问题,很
阅读:8696| 2022-11-06
我们在日常使用电脑的时候,有的小伙伴们可能在打开应用的时候会遇见提示应用程序无法
阅读:8062| 2022-11-06
今天小编告诉大家如何对win7系统打开vcf文件进行设置,可能很多用户都不知道怎么对win
阅读:8742| 2022-11-06
今天小编告诉大家如何对win10系统s4开启USB调试模式进行设置,可能很多用户都不知道怎
阅读:7595| 2022-11-06
 客服电话
客服电话
 APP下载
APP下载

 官方微信
官方微信


















请发表评论